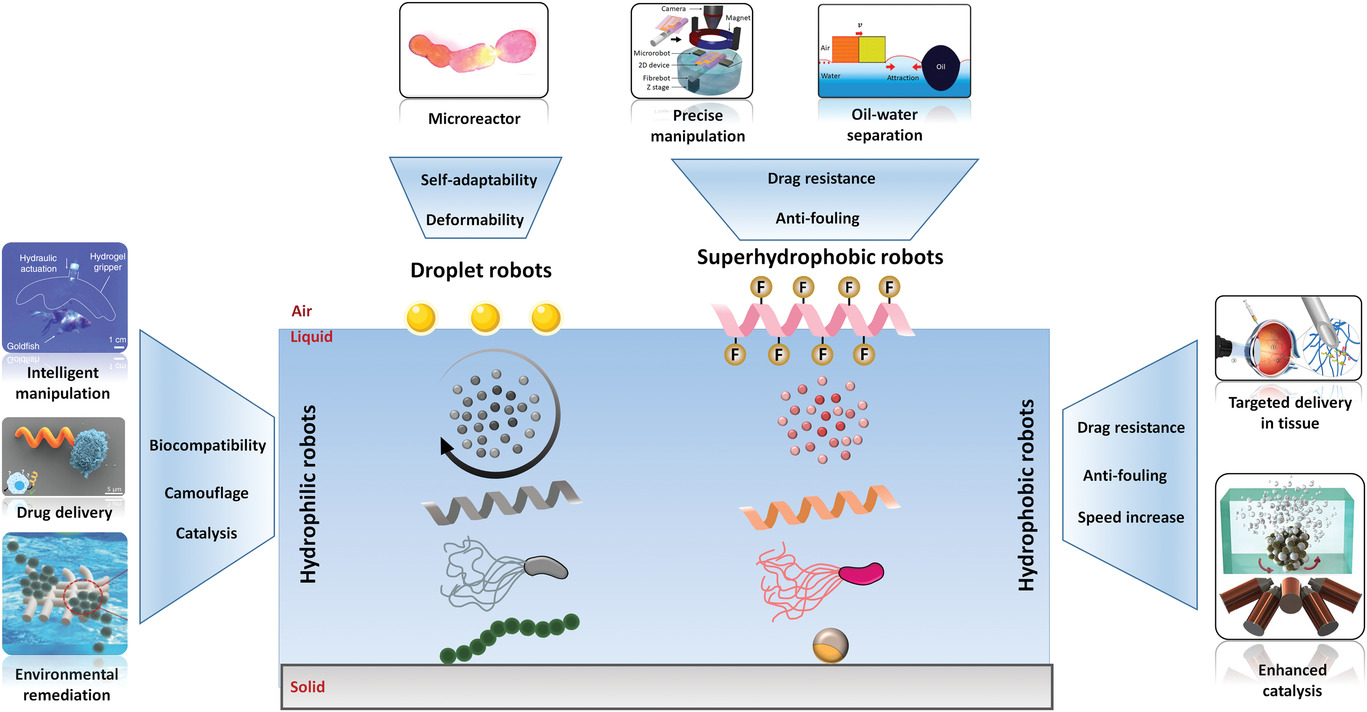
paper archives
Stay hungry, stay foolish. You are as good as your last paper.
Atomic layer deposition of electrocatalytic layer of MoS2 onto metal-based 3D-printed electrode toward tailoring hydrogen evolution efficiency
- Veronika Urbanová, Jan Plutnara, and Martin Pumera*

Molybdenum disulfide, the most representative material of transition metal dichalcogenides, has lately been considered as an attractive electrocatalyst for sustainable energy conversion and storage oriented applications. Since the electrocatalytic properties of MoS2 are extremely dependent on its structure, preparation of such material with high degree of controlled properties is at the forefront of scientific community. In this work, atomic layer deposition (ALD) was exploited for the deposition of MoS2 onto 3D-printed metallic electrodes toward hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) under the acidic condition. The observed results clearly demonstrate that the variation of the number of pulses in the ALD process has crucial impact toward the HER performance since it alters the thickness and roughness of the MoS2 films and provides highly pure deposit at the same time. Thus, one can anticipate preparation of well-defined material suitable for energy conversion applications using such deposition technique.